MicroServices - Part 3 : Spring Cloud Service Registry and Discovery
In the microservices world, Service Registry and Discovery plays an important role because we most likely run multiple instances of services, and we need a mechanism to call other services without hardcoding their hostnames or port numbers. In addition to that, in Cloud environments, service instances may come up and go down at any time. So we need some automatic service registration and discovery mechanism. Spring Cloud provides Service Registry and Discovery features, as usual, with multiple options. We can use Netflix Eureka or Consul for Service Registry and Discovery.
In this post, we will learn how to use Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka for Service Registry and Discovery.
MicroServices using Spring Boot & Spring Cloud
- Part 1: MicroServices: Spring Boot & Spring Cloud Overview
- Part 2: MicroServices: Configuration Management with Spring Cloud Config and Vault
- Part 3: MicroServices: Spring Cloud Service Registry and Discovery
- Part 4: MicroServices: Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker using Netflix Hystrix
- Part 5: MicroServices: Spring Cloud Zuul Proxy as API Gateway
- Part 6: MicroServices: Distributed Tracing with Spring Cloud Sleuth and Zipkin
In my previous post, Part 2: MicroServices: Configuration Management with Spring Cloud Config and Vault, we learned how to store configuration parameters externally in a configuration server and how to securely store secrets in Vault.
In this post, we are going to learn:
- What is Service Registry and Discovery?
- A Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka-based Service Registry
- Registering microservices as Eureka Clients
- Discovering other services using a Eureka Client
What is Service Registry and Discovery?
Suppose we have 2 microservices, catalog-service and inventory-service, and we are running 2 instances of inventory-service at http://localhost:8181/ and http://localhost:8282/. Now let’s say we want to invoke some inventory-service REST endpoint from catalog-service. Which URL should we hit? Generally, in these scenarios, we use a load balancer, configuring these 2 URLs to be delegated to, and we will invoke the REST endpoint on the load balancer’s URL. Fine.
But what if you want to spin up new instances dynamically based on load? Even if you are going to run only a few server nodes, manually updating the server node details in the load balancer configuration is error-prone and tedious. This is why we need an automatic Service Registration mechanism and to be able to invoke a service using some logical service ID instead of using a specific IP Address and port number.
We can use a Netflix Eureka Server to create a Service Registry and make our microservices Eureka Clients so that as soon as we start a microservice, it will get registered with the Eureka Server automatically with a logical Service ID. Then, the other microservices, which are also Eureka Clients, can use the Service ID to invoke REST endpoints.
Spring Cloud makes it very easy to create a Service Registry and discover other services using a Load-Balanced RestTemplate.
Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka-based Service Registry
Let us create a Service Registry using Netflix Eureka, which is nothing but a Spring Boot application with the Eureka Server starter.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
We need to add the @EnableEurekaServer annotation to make our Spring Boot application a Eureka Server-based Service Registry.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServiceRegistryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceRegistryApplication.class, args);
}
}
By default, each Eureka Server is also a Eureka client and needs at least one service URL to locate a peer. As we are going to have a single Eureka Server node (Standalone Mode), we are going to disable this client-side behavior by configuring the following properties in the application.properties file.
application.properties
spring.application.name=service-registry
server.port=8761
eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
eureka.client.registerWithEureka=false
eureka.client.fetchRegistry=false
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
Netflix Eureka Service provides a UI where we can see all the details about registered services.
Now run ServiceRegistryApplication and access http://localhost:8761, which will display a UI similar to the screenshot below.
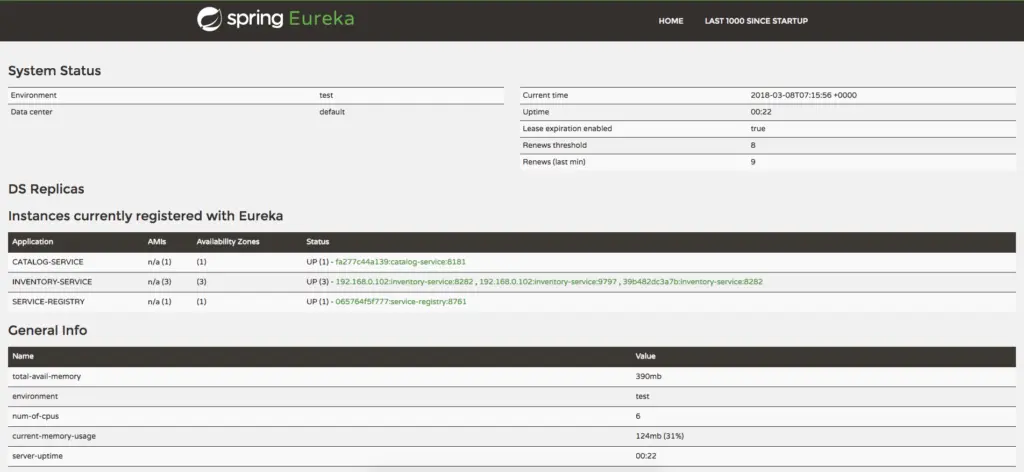
Registering microservices as Eureka Clients
In Part 2: MicroServices: Configuration Management with Spring Cloud Config and Vault,
we created a catalog-service. Let us make this service a Eureka Client and register it with the Eureka Server.
Add the Eureka Discovery starter to catalog-service, which will add the following dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
With spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client on the classpath, we just need to configure the eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone property in application.properties to automatically register with the Eureka Server.
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
When a service is registered with the Eureka Server, it keeps sending heartbeats for a certain interval. If the Eureka server doesn’t receive a heartbeat from any service instance, it will assume the service instance is down and take it out of the pool.
With this configuration in place, start catalog-service and visit http://localhost:8761.
You should see that catalog-service is registered with the SERVICE ID as CATALOG-SERVICE.
You can also notice the status as UP(1), which means the services are up and running, and one instance of catalog-service is running.
Let us start another instance of catalog-service on a different port using the following command:
java -jar -Dserver.port=9797 target/catalog-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-exec.jar
Now, if you go to http://localhost:8761, you will notice that 2 instances of catalog-service got registered, and you can see their hostname and port details as well.
Discovering other services using a Eureka Client
In the previous section, we learned how to register a service as a Eureka client, and we also tried registering multiple instances of the same service.
Now we will create another microservice, inventory-service, which exposes a REST endpoint, http://localhost:8282/api/inventory/{productCode}, which will give the currently available quantity as a response.
{
productCode: "P001",
availableQuantity: 250
}
Create the inventory-service Spring Boot application with Web, JPA, H2/MySQL, Actuator, Config Client, and Eureka Discovery starters.
Create a REST Controller to return Inventory details for a given product code.
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class InventoryController {
private final InventoryItemRepository inventoryItemRepository;
@Autowired
public InventoryController(InventoryItemRepository inventoryItemRepository) {
this.inventoryItemRepository = inventoryItemRepository;
}
@GetMapping("/api/inventory/{productCode}")
public ResponseEntity<InventoryItem> findInventoryByProductCode(@PathVariable("productCode") String productCode) {
log.info("Finding inventory for product code :"+productCode);
Optional<InventoryItem> inventoryItem = inventoryItemRepository.findByProductCode(productCode);
if(inventoryItem.isPresent()) {
return new ResponseEntity(inventoryItem, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
return new ResponseEntity(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}
Please look at the GitHub Repository for the
InventoryItem,InventoryItemRepository, etc. code.
Register inventory-service with the Eureka server by configuring the Eureka serviceUrl in src/main/resources/bootstrap.properties.
spring.application.name=inventory-service
server.port=8282
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
Now build inventory-service and start 2 instances of it by running the following commands:
java -jar -Dserver.port=9898 target/inventory-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-exec.jar
java -jar -Dserver.port=9999 target/inventory-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-exec.jar
Now you can visit the Eureka Dashboard at http://localhost:8761/ and see 2 instances of inventory-service registered.
Suppose we want to invoke the inventory-service REST endpoint from catalog-service.
We can use RestTemplate to invoke the REST endpoint, but there are 2 instances running.
We can register RestTemplate as a Spring bean with the @LoadBalanced annotation.
The RestTemplate with the @LoadBalanced annotation will internally use the Ribbon LoadBalancer to resolve the ServiceID
and invoke the REST endpoint using one of the available servers.
@SpringBootApplication
public class CatalogServiceApplication {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CatalogServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
Now we can use RestTemplate to invoke the inventory-service endpoint at http://inventory-service/api/inventory/{productCode}.
@Service
@Transactional
@Slf4j
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
public ProductService(ProductRepository productRepository, RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.productRepository = productRepository;
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
public Optional<Product> findProductByCode(String code) {
Optional<Product> productOptional = productRepository.findByCode(code);
if(productOptional.isPresent()) {
log.info("Fetching inventory level for product_code: "+code);
ResponseEntity<ProductInventoryResponse> itemResponseEntity =
restTemplate.getForEntity("http://inventory-service/api/inventory/{code}",
ProductInventoryResponse.class,
code);
if(itemResponseEntity.getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.OK) {
Integer quantity = itemResponseEntity.getBody().getAvailableQuantity();
log.info("Available quantity: "+quantity);
productOptional.get().setInStock(quantity> 0);
} else {
log.error("Unable to get inventory level for product_code: "+code +
", StatusCode: "+itemResponseEntity.getStatusCode());
}
}
return productOptional;
}
}
@Data
public class ProductInventoryResponse {
private String productCode;
private int availableQuantity;
}
Note that we have used http://inventory-service/api/inventory/{code} instead of http://localhost:9898/api/inventory/{code} or http://localhost:9999/api/inventory/{code} directly.
With this kind of automatic Service Registration and Discovery mechanism, we no longer need to worry about how many instances are running, what their hostnames and ports are, etc.
You can find the source code for this article at https://github.com/sivaprasadreddy/spring-boot-microservices-series
Summary
In this post, we learned how to use Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka for Service Registry and Discovery. In the next post, we will look at implementing the Circuit Breaker pattern using Netflix Hystrix.
References:
Related content
- MicroServices - Part 6 : Distributed Tracing with Spring Cloud Sleuth and Zipkin
- MicroServices - Part 5 : Spring Cloud Zuul Proxy as API Gateway
- MicroServices - Part 4 : Spring Cloud Circuit Breaker using Netflix Hystrix
- MicroServices - Part 2 : Configuration Management with Spring Cloud Config and Vault
- MicroServices using Spring Boot & Spring Cloud – Part 1 : Overview